初识设计模式——装饰模式(Decorator Pattern)
装饰模式(Decorator Pattern)属于结构型设计模式,它允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构。这种模式创建了一个装饰类,用来包装原有的类,并在保持类方法签名完整性的前提下,提供了额外的功能。装饰模式以对客户端透明的方式动态地给一个对象附加上更多的责任,就像给一个对象 “穿衣服” 一样,可以根据需要一层一层地添加装饰。
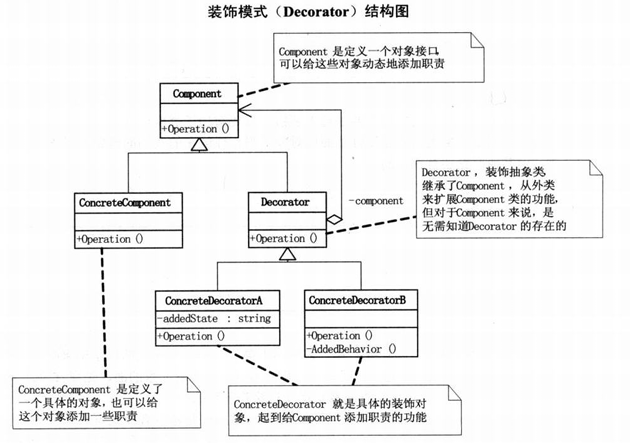
装饰模式的结构
- 抽象组件(Component):定义一个抽象接口,该接口规定了被装饰对象和装饰器对象的公共方法,客户端通过这个接口来操作对象。
- 具体组件(Concrete Component):实现抽象组件接口,是被装饰的具体对象,它定义了基本的行为。
- 抽象装饰器(Decorator):实现抽象组件接口,并持有一个抽象组件类型的引用,用于引用被装饰的对象。
- 具体装饰器(Concrete Decorator):继承自抽象装饰器,负责给具体组件添加额外的功能。

代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| <?php
interface Beverage {
public function getDescription();
public function cost();
}
class Espresso implements Beverage {
public function getDescription() {
return "浓缩咖啡";
}
public function cost() {
return 2.0;
}
}
abstract class CondimentDecorator implements Beverage {
protected $beverage;
public function __construct(Beverage $beverage) {
$this->beverage = $beverage;
}
}
class Milk extends CondimentDecorator {
public function getDescription() {
return $this->beverage->getDescription() . " + 牛奶";
}
public function cost() {
return $this->beverage->cost() + 0.5;
}
}
class Mocha extends CondimentDecorator {
public function getDescription() {
return $this->beverage->getDescription() . " + 摩卡";
}
public function cost() {
return $this->beverage->cost() + 0.7;
}
}
$beverage = new Espresso();
echo $beverage->getDescription() . ",价格:" . $beverage->cost() . " 美元\n";
$beverageWithMilk = new Milk($beverage);
echo $beverageWithMilk->getDescription() . ",价格:" . $beverageWithMilk->cost() . " 美元\n";
$beverageWithMilkAndMocha = new Mocha($beverageWithMilk);
echo $beverageWithMilkAndMocha->getDescription() . ",价格:" . $beverageWithMilkAndMocha->cost() . " 美元\n";
?>
|
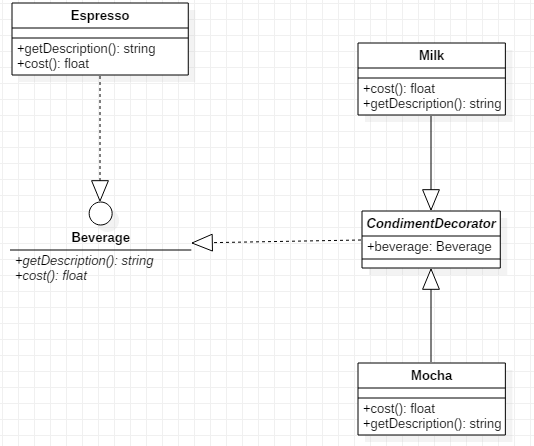
UML类图

装饰器模式的优缺点
优点
- 灵活性高:可以在运行时动态地为对象添加或移除功能,而不需要修改原对象的代码,符合开闭原则。
- 可扩展性强:通过创建新的装饰器类,可以轻松地添加新的功能,而不会影响到现有的代码。
- 避免子类爆炸:相比于使用继承来扩展功能,装饰模式可以避免创建大量的子类,减少代码的复杂性。
- 单一职责原则:每个装饰器只负责一个特定的功能,使得代码更加清晰和易于维护。
缺点
- 对象嵌套过多:如果使用多个装饰器,会导致对象嵌套层次过深,增加代码的复杂度和理解难度。
- 调试困难:由于装饰器的嵌套,可能会让调试和维护变得更加困难,尤其是在出现问题时,难以定位具体是哪个装饰器导致的问题。
- 性能开销:多层装饰会增加对象的创建和调用的开销,可能会对性能产生一定的影响。
值得注意的问题
在装饰模式中,过度装饰会导致对象嵌套层次过深、代码复杂度增加以及调试和维护困难等问题。以下是一些避免过度装饰的方法:
1. 明确业务需求和功能边界
在使用装饰模式之前,要对业务需求进行详细分析,明确哪些功能需要通过装饰器来添加,以及每个装饰器的具体职责。制定合理的功能边界,避免为了追求灵活性而添加过多不必要的装饰器。
2. 限制装饰器的使用
设置最大装饰层数:在代码中可以通过某种机制来限制装饰器的嵌套层数。例如,在装饰器的构造函数中添加检查逻辑,如果嵌套层数超过预设的最大值,则抛出异常。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| <?php
interface Beverage {
public function getDescription();
public function cost();
}
class Coffee implements Beverage {
public function getDescription() {
return "咖啡";
}
public function cost() {
return 5;
}
}
abstract class CondimentDecorator implements Beverage {
protected $beverage;
protected $decoratorLevel = 0;
const MAX_DECORATOR_LEVEL = 3;
public function __construct(Beverage $beverage) {
if ($beverage instanceof CondimentDecorator) {
$this->decoratorLevel = $beverage->decoratorLevel + 1;
if ($this->decoratorLevel > self::MAX_DECORATOR_LEVEL) {
throw new Exception("超过最大装饰层数");
}
}
$this->beverage = $beverage;
}
}
class Milk extends CondimentDecorator {
public function getDescription() {
return $this->beverage->getDescription() . " + 牛奶";
}
public function cost() {
return $this->beverage->cost() + 2;
}
}
class Sugar extends CondimentDecorator {
public function getDescription() {
return $this->beverage->getDescription() . " + 糖";
}
public function cost() {
return $this->beverage->cost() + 1;
}
}
try {
$coffee = new Coffee();
$coffeeWithMilk = new Milk($coffee);
$coffeeWithMilkAndSugar = new Sugar($coffeeWithMilk);
$overDecorated = new Milk($coffeeWithMilkAndSugar);
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
?>
|
在上述代码中,CondimentDecorator 抽象类中定义了最大装饰层数 MAX_DECORATOR_LEVEL,并在构造函数中检查当前装饰层数是否超过最大值,如果超过则抛出异常。
3. 采用组合替代嵌套
可以将多个相关的装饰器组合成一个新的装饰器,而不是进行多层嵌套。这样可以减少嵌套层次,提高代码的可读性和可维护性。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| <?php
interface Beverage {
public function getDescription();
public function cost();
}
class Coffee implements Beverage {
public function getDescription() {
return "咖啡";
}
public function cost() {
return 5;
}
}
abstract class CondimentDecorator implements Beverage {
protected $beverage;
public function __construct(Beverage $beverage) {
$this->beverage = $beverage;
}
}
class Milk extends CondimentDecorator {
public function getDescription() {
return $this->beverage->getDescription() . " + 牛奶";
}
public function cost() {
return $this->beverage->cost() + 2;
}
}
class Sugar extends CondimentDecorator {
public function getDescription() {
return $this->beverage->getDescription() . " + 糖";
}
public function cost() {
return $this->beverage->cost() + 1;
}
}
class MilkAndSugar extends CondimentDecorator {
public function getDescription() {
return $this->beverage->getDescription() . " + 牛奶 + 糖";
}
public function cost() {
return $this->beverage->cost() + 3;
}
}
$coffee = new Coffee();
$coffeeWithMilkAndSugar = new MilkAndSugar($coffee);
echo $coffeeWithMilkAndSugar->getDescription() . ",价格:" . $coffeeWithMilkAndSugar->cost() . " 元\n";
?>
|
在这个例子中,创建了一个新的组合装饰器 MilkAndSugar,将添加牛奶和糖的功能组合在一起,避免了多层嵌套。
4. 遵循单一职责原则
每个装饰器应该只负责一个明确的功能,避免一个装饰器承担过多的职责。这样可以使代码更加清晰,易于理解和维护。如果一个装饰器承担了过多的职责,当需要修改其中一个功能时,可能会影响到其他功能。